What is Edge Computing?
Last updated on September 9th, 2023 at 08:18 am
What is Edge Computing
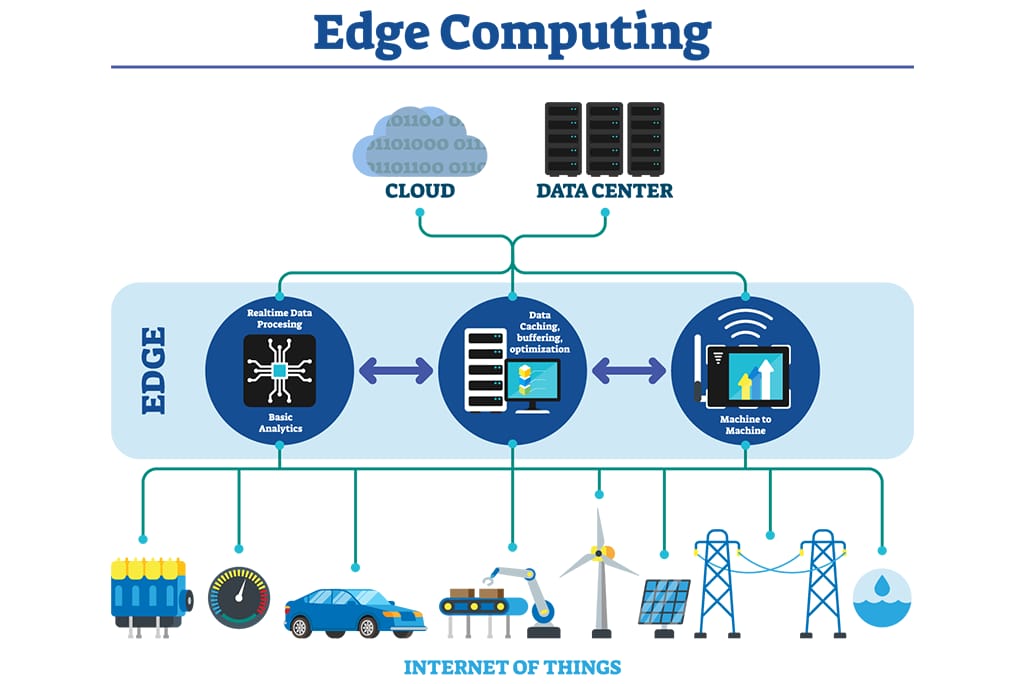
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the devices or systems that produce and consume data, reducing latency and bandwidth usage, enhancing reliability, and improving efficiency. Here are some key points to understand the concept of edge computing in more detail:
1. Edge computing involves processing and storing data at or near the edge of the network, where the data is generated or consumed, instead of sending it to a centralized data center or cloud environment.
2. Edge devices include sensors, smart appliances, cameras, autonomous vehicles, drones, and other IoT devices that collect and transmit data over a network.
3. Edge computing can enable real-time analytics, predictive maintenance, automation, and other applications that require low latency, high bandwidth, or high reliability.
4. Edge computing architectures can be decentralized, where each edge device has its own processing and storage capabilities, or centralized, where a cluster of edge devices is managed by a central controller or cloud-based system.
5. Edge computing can leverage a variety of technologies, including machine learning, containerization, serverless computing, blockchain, and edge gateways, to enable efficient and secure data processing and storage.
6. Edge computing can be implemented in various domains, including industrial IoT, smart cities, healthcare, retail, transportation, and more.
7. Edge computing can have significant benefits, such as reducing network congestion, improving data privacy and security, reducing data transfer costs, and enabling new business models and revenue streams.
Overall, edge computing represents a fundamental shift in the way data processing and storage is done, offering new opportunities and challenges for organizations and individuals to leverage the power of distributed computing.
Here are some additional details and insights about Edge Computing:
1. Edge computing can be thought of as an extension of cloud computing, where some of the computing and storage resources are moved closer to the data source or end-user device. This can help reduce the load on centralized data centers, improve responsiveness, and enable more efficient use of resources.
2. The rise of IoT devices and the proliferation of data generated by them has created a need for edge computing. By processing data at the edge, organizations can avoid sending large amounts of data back and forth to the cloud, reducing network latency and improving overall performance.
3. In addition to reducing latency and improving performance, edge computing can also enhance data privacy and security. By processing data locally, organizations can reduce the risk of sensitive data being exposed to potential attackers or hackers.
4. There are several different deployment models for edge computing, including device-level, gateway-level, and regional-level architectures. Each of these models has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice will depend on factors such as the size of the network, the nature of the applications, and the specific requirements of the organization.
5. Edge computing can enable a range of use cases, from predictive maintenance in industrial settings to real-time video analytics in retail environments. By enabling faster and more accurate data analysis, edge computing can help organizations make better decisions and improve operational efficiency.
6. There are some challenges associated with implementing edge computing, including the need for standardized protocols, the complexity of managing distributed computing resources, and the potential for increased security risks. Organizations must carefully evaluate these challenges and develop appropriate strategies for addressing them.
7. Overall, edge computing represents a significant opportunity for organizations to unlock the full potential of their data and improve their operational performance. As more and more devices become connected to the internet, the importance of edge computing is likely to continue to grow.